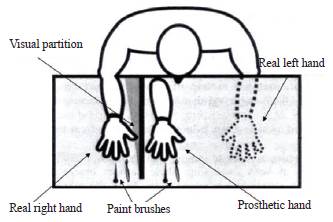
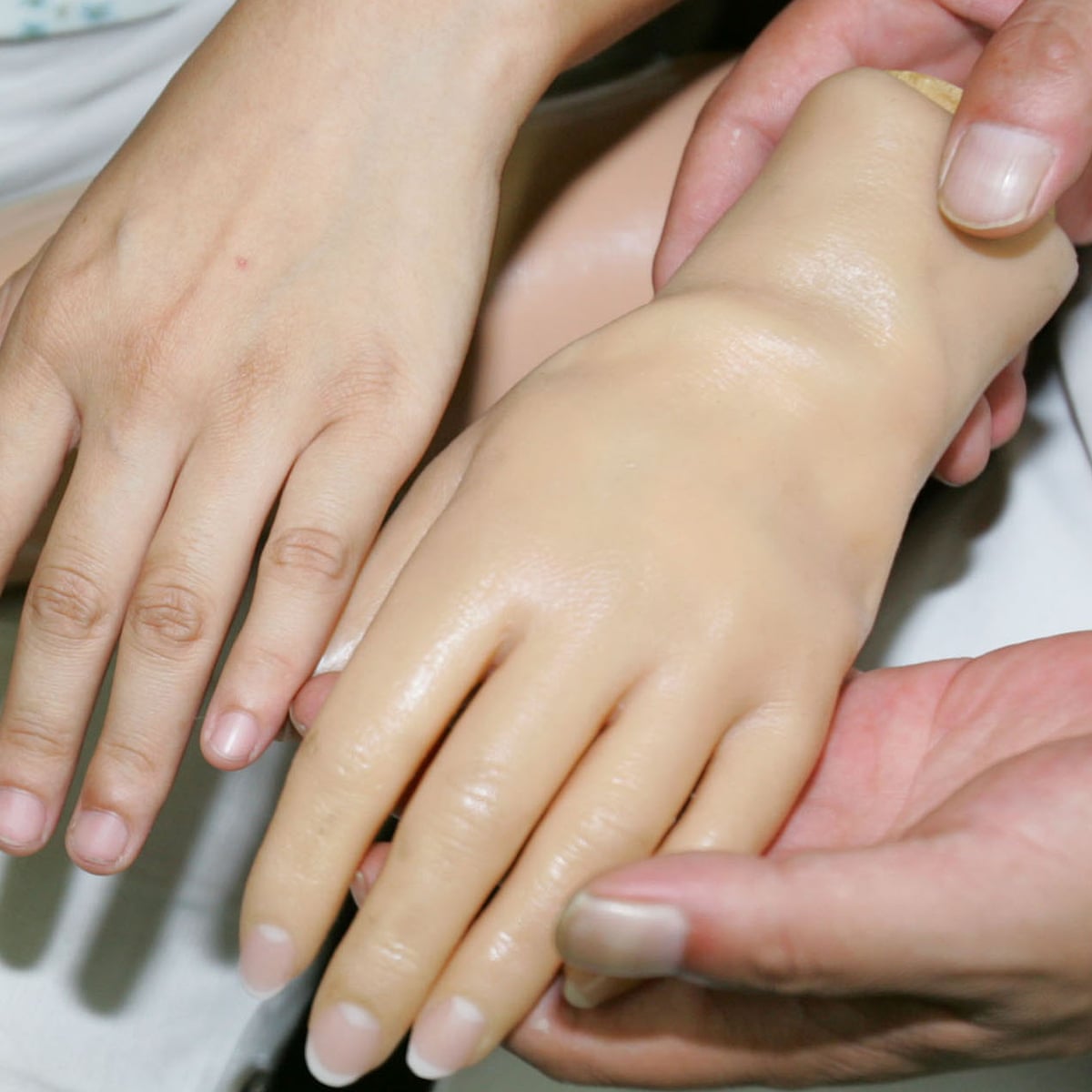
This video will demonstrate how to induce this body transfer trick called the rubber hand illusion where a fake limb is perceived as being real using methods originally devised by botvinick and cohen.
Rubber hand illusion phantom limb.
Lenggenhager et al 2007.
The mirror box gives visual feedback that can allow a person using it the opportunity to see the missing hand and to manipulate the hand in an attempt to relieve pain or discomfort.
Rubber hand illusion reveals how the brain understands the body.
In our daily life the sense of body ownership is a fundamental aspect of self consciousness.
Surprisingly in the present modified rubber hand illusion we found that simultaneous stroking or stimulation of the participant s.
Blanke et al 2015 one potent example is the well studied rubber hand illusion rhi botvinick and cohen 1998.
However in the present investigation in which phantom limb illusions within body space are induced and manipulated we found that perceiving phantom sensations and illusory embodiment does not require amputation.
The bodily boundaries in amputees may seem to be more malleable than in non amputees given the propensity for a phantom limb to embody a mirror reflected hand.
The representation of body ownership usually relies on integration of information from multiple sensory modalities ehrsson 2007.
It will also investigate how such an experience can be applied for instance to the treatment of phantom limb pain.
Now researchers find not even a rubber hand is needed to create an illusion of a phantom limb.
Body transfer illusion has been used in order to treat the experience of phantom limb pain by giving visual feedback of the missing limb.
Scientists performed the rubber hand illusion.